Mars Globe HD
App Developer: Midnight Martian
Version 2.2.1
License:US$0.99 (Mars Globe Free) Compatible with iPhone 3GS, iPhone4, iPhone4S, iPod (3rd and 4th generations) and iPad. Requires IOS 3.2 or later.

The Mars Globe HD app is an enjoyable astronomy tool that you can use to learn about the planet Mars and the many space missions that have landed on its surface. The application has been recently updated to run at full resolution on the new iPad.
I’m a volunteer telescope operator at the Flandrau Science Center in Tucson, Arizona. I, along with about a dozen other volunteer telescope operators, take turns several times a month showing the night sky to the public through the Center’s sixteen inch Cassegrain reflector telescope.
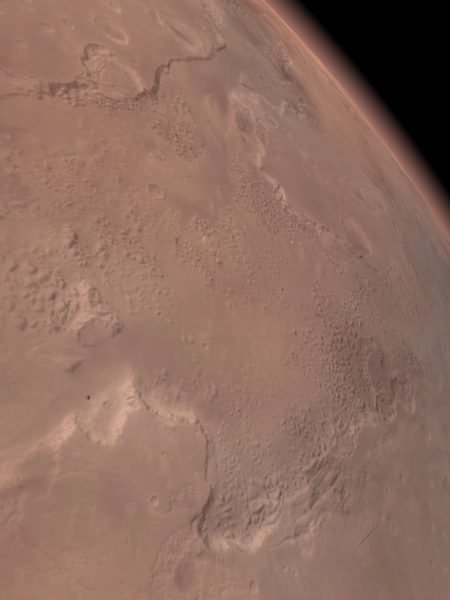
The planet Mars has recently passed through opposition to the Sun, which means it is closer to Earth at this time as we orbit the Sun. Rising in the eastern evening sky it appears as a bright, rusty colored star-like object. Observing Mars through the Center’s telescope we can only see some of the subtle coloration details on the surface of this small planet that is roughly half the size of Earth and over seventy-seven million miles away. These subtle variations in color are associated with surface features such as craters, mountains, valleys, and surface materials.
This year is a special year for Mars exploration because we have the Mars Science Laboratory, a rover named Curiosity, en route to the planet and scheduled to land in early August. We can use the Mars Globe HD app to show what those surface details are and even check out where Curiosity is targeted to land.

At the top of the display, the Control Bar offers, from left to right, View Options button, selection of Labels button, Search Fields button, Options button for Sound on/off and Draw Atmosphere, Mars Globe HD information button, and Time Zone control button. Tapping the display with one finger allows you to cover or uncover the Control Bar as well as the various labels you have selected.
For details on how to use the application, just tap the Mars Globe HD information button, which is a circled question mark, and you are presented with a display panel as illustrated in figure 2. In addition, information about the application, an introduction to the planet Mars, and a host of web links for more information regarding the exploration of Mars are provided.
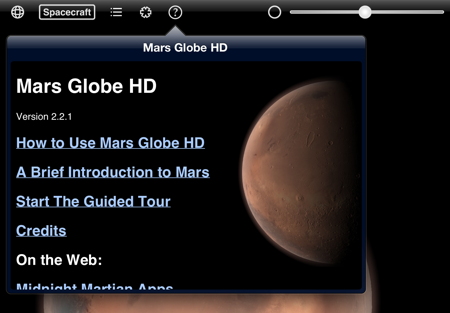
Tapping the Mars Globe HD information button again closes the panel. The slider bar on the upper top left is used to vary the direction of the sunlight on the globe of Mars. This allows you to rotate the globe and view the entire surface in daylight. Tapping the button to the left of the slider bar selects Time Zone. With theTime Zone selected, you can rotate the globe and the planet will rotate from daytime to nighttime.
For this review I want to check out where our current Mars lander is going. Using the Mars Science Laboratory website, I learned that the spacecraft is targeted to land in the Gale Crater. By tapping the Labels button at the top left, we get the Labels panel and I select Highlights. I then tap the Search Fields button, third left from top, and get the search panel. I then type in Gale Crater and tap on the displayed result, and the application takes us to the location of the crater. Tap again on the Crater label and additional information is provided as shown in figure 3.

By simply tapping the Projected view over Gale Crater link we can view even more details of the crater through the web information shown in figure 4.

The application allows us to zoom only in to an altitude of 300 kilometers above the surface of Mars so these web links help us to see details at even higher resolution than the application provides. Until Curiosity lands at Gale Crater, this level of surface details will have to suffice for the present. To get an idea as to what surface details we might see after Curiosity is operating on the surface let’s visit the Phoenix Mars Lander site using the Mars Globe app.
First we tap the Labels button again, select Spacecraft, then tap the Search Fields button and select Phoenix. We are then taken to the lander’s location near the north polar ice cap of Mars as shown in figure 5.
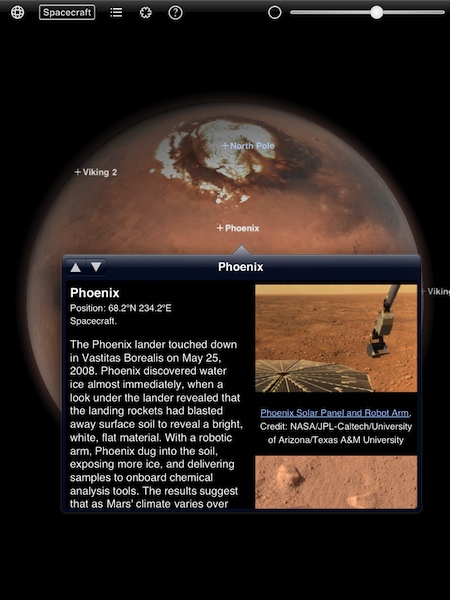
If we scroll down the information panel we can see, in figure 6, the water ice exposed just below the surface that was excavated by the robotic arm on the lander. If all goes well with Curiosity, I hope we will see details like this in future updates to the Mars Globe HD app. I plan to check the App Store for any updates after Curiosity successfully lands and begins operating at Gale Crater.

Mars Globe HD is a real bargain at only US$0.99 and is also available in a free version simply called Mars Globe. They both work well on my new iPad and my iPod Touch 4th generation. Therefore, I am awarding this application a MyMac.com 9 out of 10.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.